论文阅读 - EMVS: Event-Based Multi-View Stereo
EMVS: Event-Based Multi-View Stereo—3D Reconstruction with an Event Camera in Real-Time 描述了一种利用 Event Camera 的高速特性,提出的一种 MVS 方法。将传统 MVS 的 Space-Sweep 方法应用到 Event-based MVS 中。
EMVS: Event-Based Multi-View Stereo—3D Reconstruction with an Event Camera in Real-Time
Rebecq, H., Gallego, G., Mueggler, E., Scaramuzza, D.,
EMVS: Event-Based Multi-View Stereo—3D Reconstruction with an Event Camera in Real-Time,
Int. J. of Computer Vision (IJCV), 126 (12):1394-1414, 2018. PDF, YouTube, Code.
简介
本篇 paper 主要描述了一种利用 Event Camera 的高速特性,提出的一种 MVS 方法。将传统 MVS 的 Space-Sweep 方法应用到 Event-based MVS 中;在 Event-based 场景运用 Space-Sweep 具有天然的优势:
-
Event Camera 本来就是检测的场景中的 edge。
-
Event Camera 相比于固定帧率的传统 Camera,viewpoints 更加的稠密。
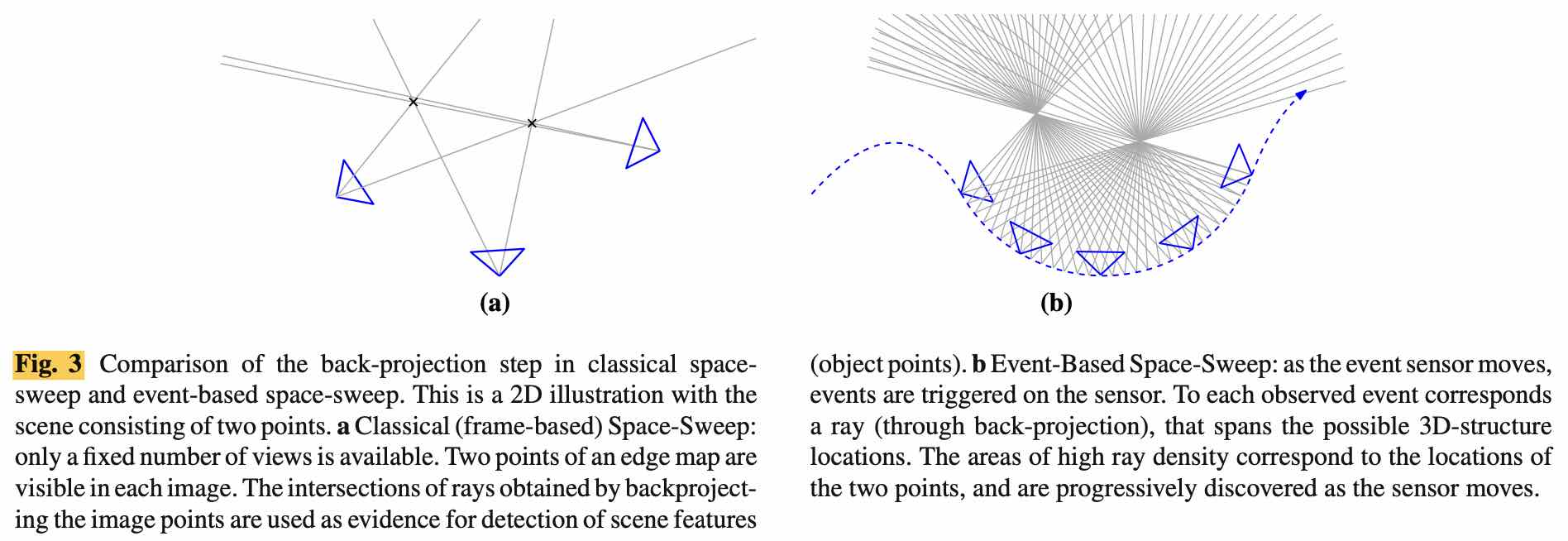
文章的整体思路简而言之,就是将 “每一帧” 的 Events 进行反投影得到了一束光线,通过计算经过 DSI 空间中每一个 voxel 的光线的数量,高于一个阈值即可确定为一个空间的 3D 点。具体实施起来,分为下文中的五步。
完整的公式推导见原论文。
主要过程
Feature-Viewing Rays by Event Back-Projection
将每一个 Event 进行反投影,得到一条光线。
This higher abundance of measurements and viewpoints in the event-based setting generates many more viewing rays than in frame-based MVS, and therefore, it facilitates the detection of scene points by analyzing the regions of high ray density.
A major advantage of our method is that no explicit data association is needed.
不需要 Event 之间的数据关联、不需要 intensity 信息。
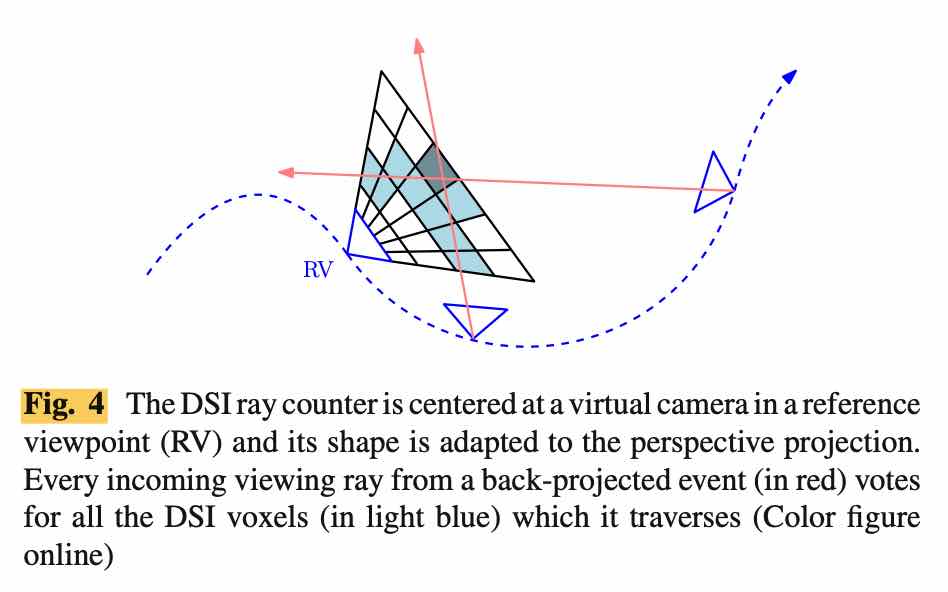
Volumetric Ray Counting. Creating the Disparity Space Image (DSI)
在 DSI 中进行计数。这个时候问题就来了,如何确定这个 DSI 空间呢?
作者考虑到 the reconstruction of large scenes in a scalable way,采用了一个分批的方式,将一组 Event 归位一批,选取一个虚拟帧 RV,基于它做一个 local 3D reconstruction。
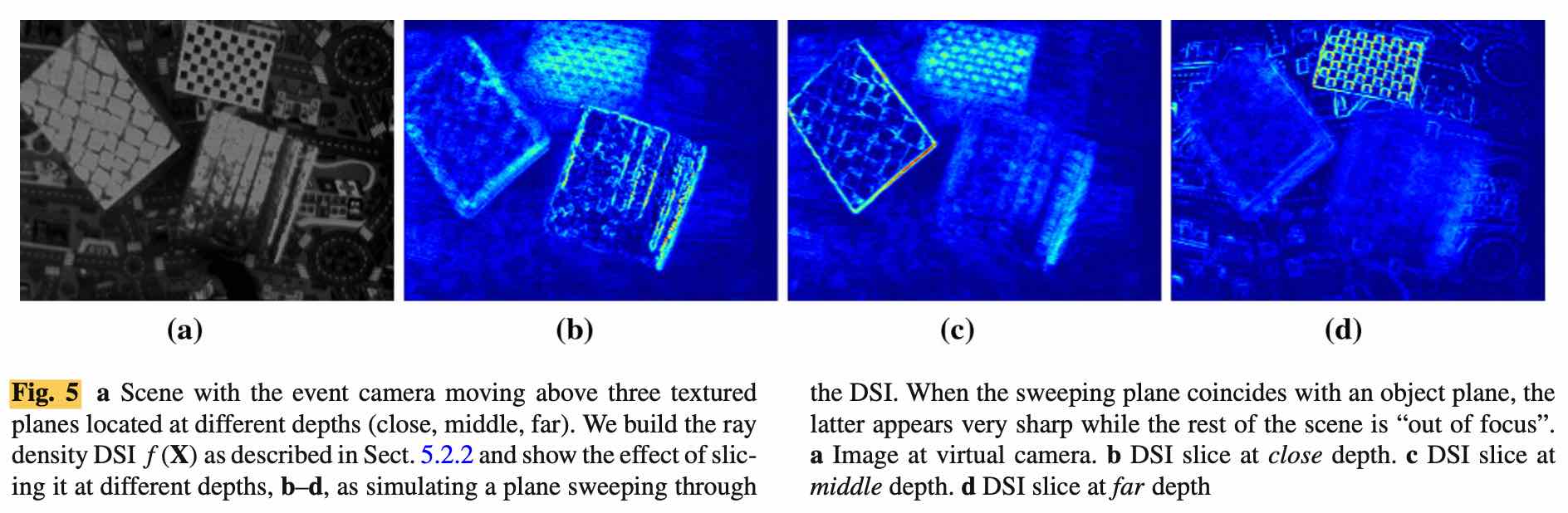
Detection of Scene Structure by Maximization of Ray Density
Local DSI 建立好之后,就卡一个阈值,是一个 local maxima 的操作。一个 DSI 的实例以及使用 local maxima 而不是 global maxima 的原因如下:
作者使用了一个 Adaptive Gaussian 阈值函数:
a pixel is selected if , with . In practice, we use a 5×5 neighborhood in and = −10
从 DSI 中提取结构:
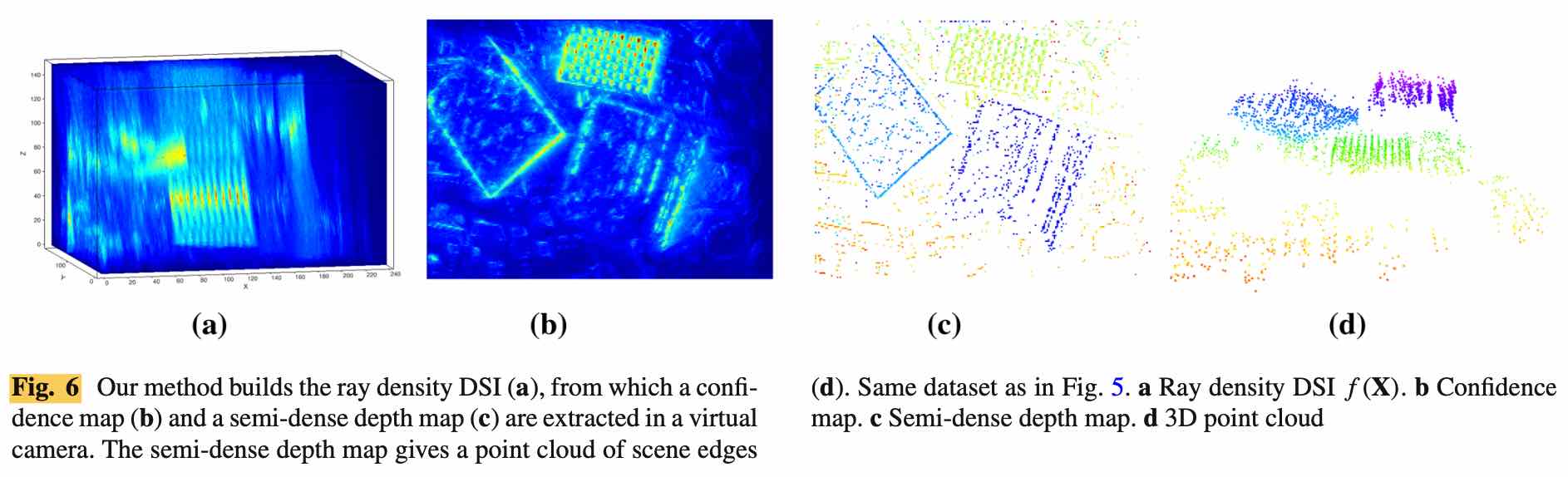
Merging Depth Maps from Multiple Reference Viewpoints
既然有了上面提到的 Local reconstruction,那么就肯定有 key frame 的概念和一次 local 的大小的确定。
we select a new key reference view as soon as the distance to the previous key reference view exceeds a certain percent- age of the mean scene depth (typically a number between 15 and 40%), and use the subset of events until the next key ref- erence view to estimate the corresponding semi-dense depth map of the scene.
然后再做滤波去除一些噪声。融合的话,有了每组 local 点云的 pose ,有很多的方法就可以选了。
Map Cleaning
为了得到更好的效果,又进一步做了滤波。
we use a median filter on the semi-dense depth maps
we also apply a radius filter (Rusu and Cousins 2011) to the final point cloud, which discards the points whose number of neighbors within a given radius is less than a threshold.
细节
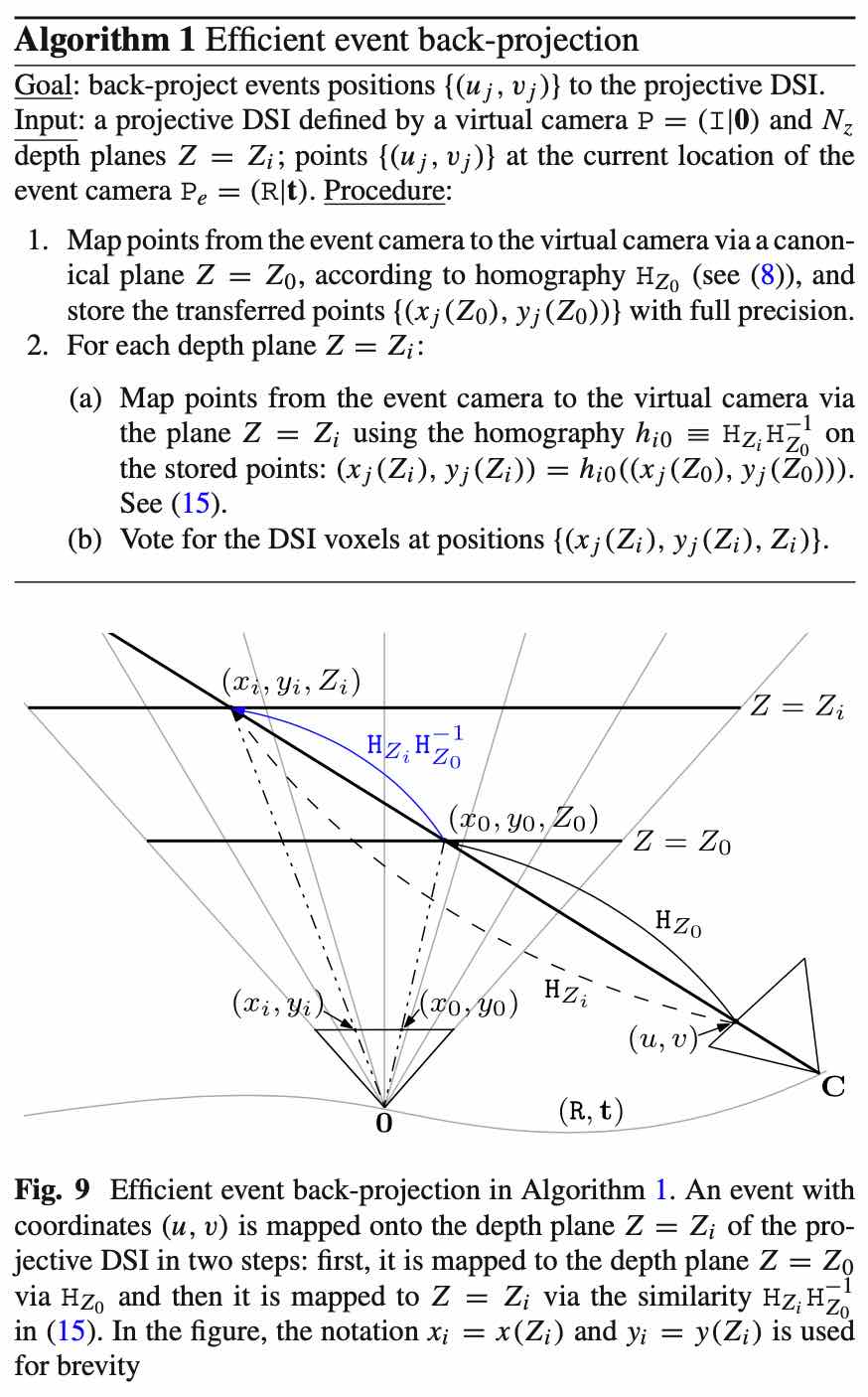
实现实时、高效的 Event 反投影到 DSI 中
主要思路:DSI 是由不同 depth 的平面们组成的,也就是说明只有 translation,无 rotation。那么,求出一个相机的当前帧与一个深度为 的 plane 之间的 homography,与其他 DSI 中的深度为 的 plane 的 homography 就可以很简单的来计算,可以推导为一步公式。
相机平面、EV 虚拟相机平面、不同深度 DSI 平面之间的关系:
其中, 为平面法向量,因为与 EV 相机平面垂直,所以为 ,在后面的公式化简中有用到。
令 ,通过展开、以及利用 性质,
进一步代入上面几个平面的关系,化简得:
其中 。
至此,计算效率就提高上来了。
算法流程:
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!联系作者。